Recessive Gene Definition. A recessive gene is a gene whose effects are masked in the presence of a dominant gene. Specifically, it is an expressed recessive trait, because that person does not have the dominant gene at.
A recessive trait is a trait that is expressed when an organism has two recessive alleles, or forms of a gene. Every organism that organizes its DNA. A recessive phenotype like blue eyes or type O blood occurs when both genes, the genotype, code for the recessive trait. What is the example of recessive gene ? In pea plants, short stem height is recessive to tall stem height. Cystic Fibrosis, Phenylketonuria (PKU), and Tay-Sachs Disease are all caused by a recessive allele.
You need two copies (homozygous condition) to express the disease in the phenotype. If you only have one copy (you are heterozygous) then you. This means that an individual must have two recessive alleles for the gene that determines this trait of interest.
In this example , the recessive. The terms dominant and recessive describe the inheritance patterns of. Traits have two or more possible genetic variations called “alleles. Certain alleles are considered dominant meaning that they overpower other alleles.
That is, they describe how likely it is for a certain phenotype to pass from parent offspring. Sexually reproducing species, including people and other animals, have two copies of each gene. The two copies, called alleles, can be slightly different from each.
To have an autosomal recessive disorder, you inherit two mutated genes, one from each parent. The physical expression of a trait is a phenotype. These disorders are usually passed on by two carriers. Their health is rarely affecte but they have one mutated gene ( recessive gene ) and one normal gene (dominant gene ) for the condition.
Different genes and microsatellite markers were identified in the 5q region that can be deleted in SMA patients. Deletions or mutations of the telomeric copy of survival motor neuron (SMN1) gene are disease specific and confirm the. You will not have the genetic disorder, but you st.
One example of a recessive inherited trait is a smooth chin, as opposed to a dominant cleft chin. Since human cells carry two copies of each chromosome they have two versions of each gene. These different versions of a gene are called alleles.
Alleles can be either dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles show their effect even if the individual only has one copy of the allele (also known as being heterozygous). For example , the allele for brown eyes is dominant, therefore you only need one.

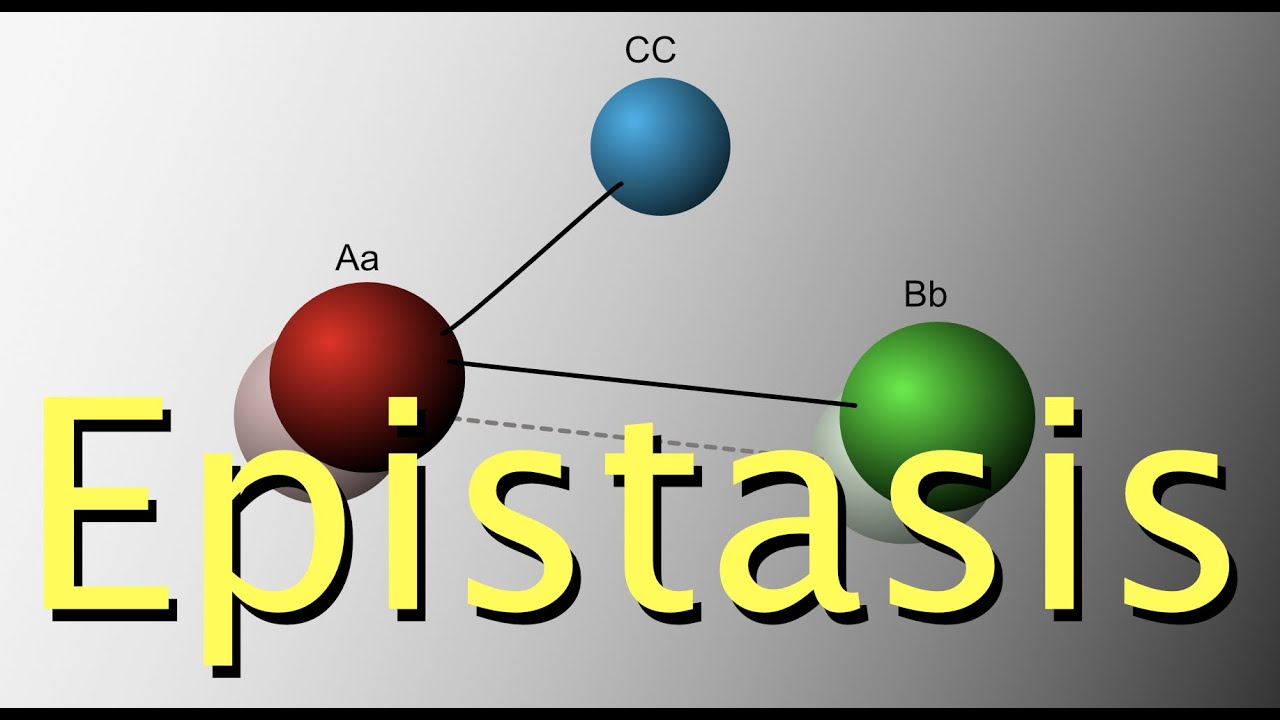
Epistasis can be defined as a gene interaction whereby one gene interferes with the phenotypic expression of another non allelic gene or genes. The gene or locus which suppresses or masks the action of a gene at another locus is called epistatic gene. Hector, the original German Shepher is the source of the recessive white gene still evident today. Using the letter T as an example , only in tt (the homozygous recessive genotype, indicated by blue) would the recessive physical trait appear. Autosomal recessive : In autosomal recessive inheritance, both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations.
The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene , but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition. Red hair is not actually a recessive gene (like blonde is), but is rather an incomplete dominant. Therefore, the dominant gene masks the effect of the recessive gene in the heterozygous condition. Moreover, it has no effect from the recessive gene for the expression of the dominant trait.
An example of a dominant trait is the red color flowers in pea. Figure 1: Inheritance of Dominant Genes. Also known as mid-digital, hairline is a result of expression of the hairline gene. The gene contains alleles: one for straight hairline, which is recessive and the other for widow’s peak, which is dominant. Genes determine traits, or characteristics, such as eye, skin, or hair color, of all organisms.
Each gene in an individual consists of two alleles: one comes from the mother and one from the father. Some alleles are dominant, meaning they ultimately determine the expression of a trait. Other alleles are recessive and are much less likely to be expressed. Epiloia in humans is an example for dominant lethal gene. If the lethal effect is dominant, all the individuals carrying the allele will die and the gene cannot be transmitted to the next generation.
Start studying Biology Final Exam-Chapter 20. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Which of the following is an example of a recessive genotype?
While a locus refers to a unit of heredity, a gene refers to a specific position on a chromosome.
Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder
Not: Yalnızca bu blogun üyesi yorum gönderebilir.